Do I have golfer’s elbow?
Golfer’s elbow is also known as medial epicondylitis. The primary symptom is pain on the inner elbow caused by repetitive motion. If you have pain in your outer elbow, it might be a condition known as tennis elbow.
Who gets golfer’s elbow?
Not just golfers! Anyone can have golfer’s elbow, but it primarily affects people who play golf, racquet sports (tennis, badminton, etc.), throwing sports, football, or bowling. It can also occur in people who lift weights or are carpenters.
What causes golfer’s elbow?
Golfer’s elbow is a repetitive stress injury (RSI). Repeatedly straightening your elbow causes damage to the muscles and tendons that control your wrist and fingers. In golf, this injury typically results from gripping and swinging your clubs incorrectly or too forcefully. It can also occur if you take thick divots.
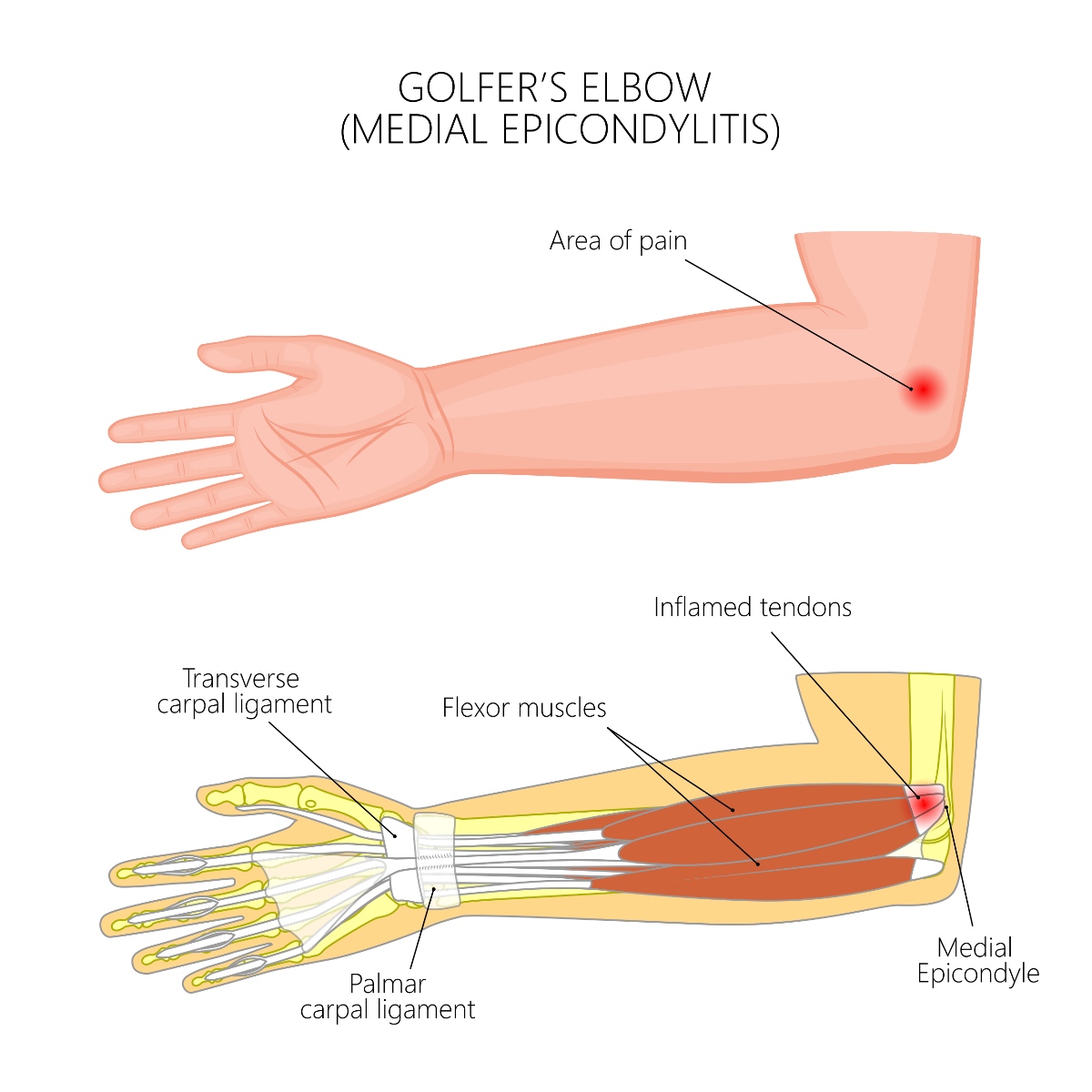
What are the symptoms?
- Pain and tenderness on the inner side of your elbow, sometimes extending down your forearm
- Elbow stiffness
- Pain when making a fist
- Weakness in your hands and wrist
- Tingling or numbness, at times radiating into the fingers
When should I see a doctor?
Seek immediate care if:
- The pain is severe
- Your elbow is warm and inflamed and you have a fever
- You think you’ve broken a bone
- Your elbow looks deformed or begins to swell less than 30 minutes after injury
- You can’t bend your elbow
- You have signs of nerve damage
- Numbness
- Pale or blue skin
- Your elbow is cold
Check with your doctor
- Before beginning a new exercise plan to treat golfer’s elbow
- If the pain continues after two weeks of home treatment
- If treatment makes your pain worse
How do I treat golfer’s elbow?
- Cold therapy or topical analgesics, like Biofreeze, can provide immediate pain relief
- While golfing or doing the activity that causes you pain, wear a support strap
- For long-term pain relief, try these exercises to relieve golfer’s elbow pain
References
Kaspriske, R. (2017, March 17). The best therapy ever for elbow tendinitis. Retrieved from http://bit.ly/2l1Us9w
Medical Disclaimer: The information provided on this site, including text, graphics, images and other material, are for informational purposes only and are not intended to substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other healthcare professional with any questions or concerns you may have regarding your condition.








 France
France Australia
Australia