The present study, aimed to identify the most effective high-resistance strength training strategy to improve body composition, lower resting blood pressure, and optimize metabolic parameters in older adults at risk of metabolic syndrome (MetS).
The results of this study were published in early 2025, and this article is meant to serve as a synopsis. A complete account of the study can be found here.
This is the first study in the world to use an innovative elastic band training method based on accentuated eccentric actions. Additionally, both this cutting-edge method and the more traditional maximal strength training approach were conducted exclusively using CLX elastic bands.
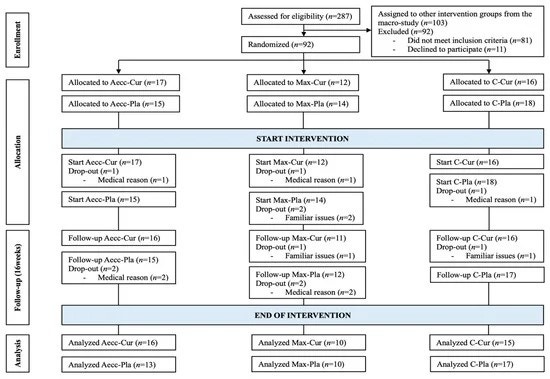
81 participants completed this study, all within the age range of 62-72. They were all classified as being at risk for MetS, based on a BMI exceeding 25 kg/m2 and systolic blood pressure readings above 130 mmHg in three experimental groups.
Participants were eligible for inclusion in the study if they met the following criteria:
- Sedentary adults aged 60 or older
- Functionally independent (able to walk 100 m unaided and climb 10 steps without resting)
- Held a medical certificate confirming suitability to enroll in RT
- Had refrained from taking antioxidant supplements (e.g., vitamins C, E, A, omega-3, etc.) for at least six weeks before the study began
- Were non-smokers and non-alcoholics
Below is an illustration that summarizes the study procedures:
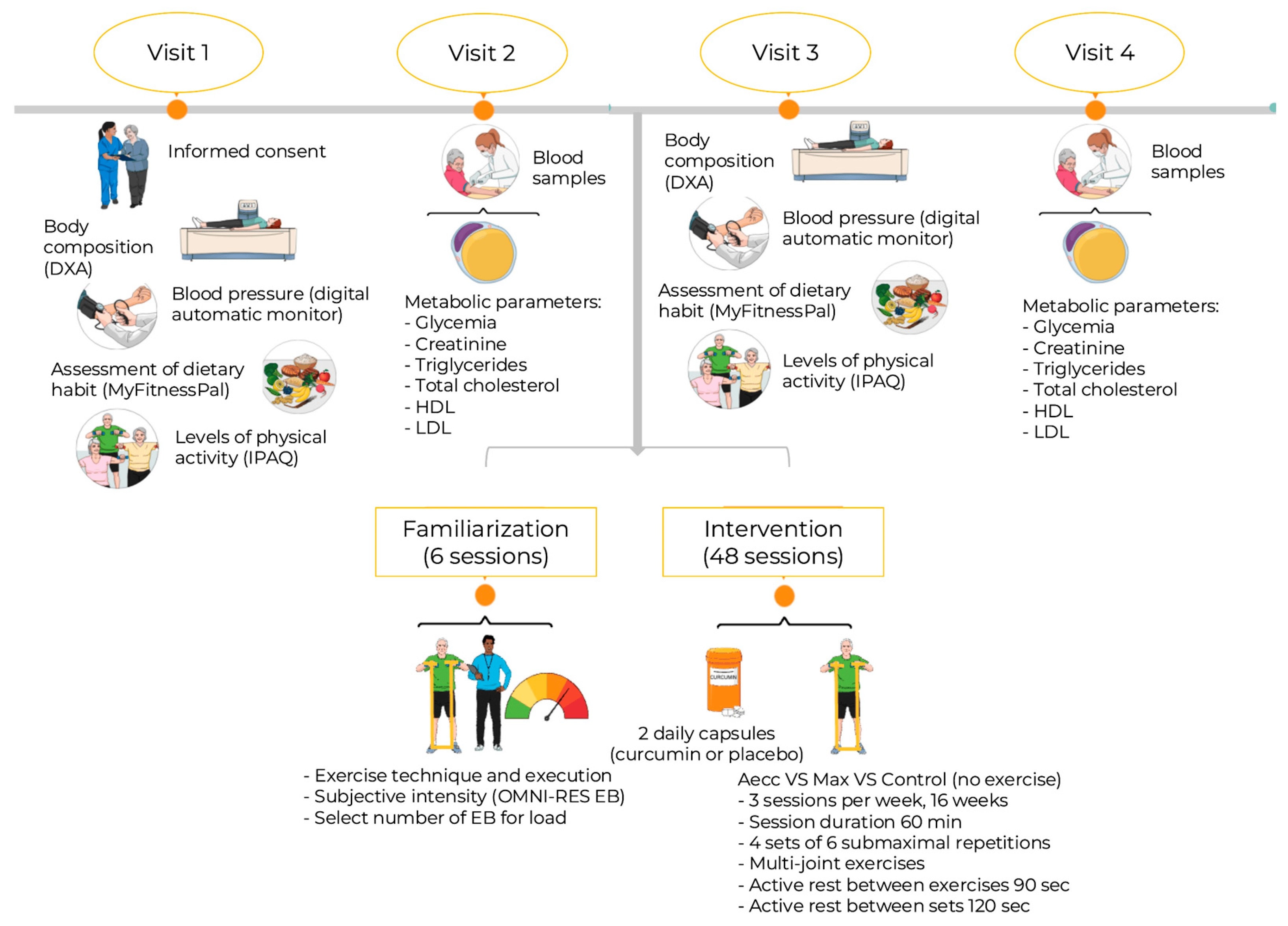

Main Findings:
- Body Composition: Both high-resistance strength training methods led to significant reductions in fat mass and increases in muscle mass. However, the group that trained maximal strength using the traditional method and also took curcumin achieved superior fat mass reduction compared to the other groups, while muscle mass gains were similar across all groups (ranging from 1.4% to 2.3%).
- Blood Pressure: Significant and comparable reductions were observed in systolic blood pressure (ranging from 9.8% to 11.4%) and diastolic blood pressure (ranging from 6.3% to 10.4%) across all strength training groups.
- Metabolic Parameters: Both training methods significantly improved metabolic parameters, with similar improvements observed across experimental groups. The only exception was creatinine levels, which showed a significant increase post-training in the maximal strength + curcumin group compared to the other groups.
- Effect of Curcumin Supplementation: Curcumin supplementation enhanced the positive effects of strength training across all evaluated variables, except for creatinine levels.
- Clinical Impact: Between 54% and 100% of participants achieved clinically relevant improvements in 7 out of 10 dependent variables across all experimental groups.
Below is a flowchart of participant flow throughout the study:

Conclusion: High-resistance strength training programs exclusively using CLX elastic bands, combined with curcumin supplementation, led to significant improvements in body composition, blood pressure, and metabolic parameters in older adults at risk of metabolic syndrome, with no observed adverse effects. While both training methods were effective, the group that trained maximal strength using the traditional approach and also took curcumin achieved greater reductions in fat mass, suggesting that this strategy may be the most recommended for optimizing body composition. However, an increase in creatinine levels was observed in this group, so caution is advised for individuals with pre-existing renal conditions until the clinical significance of this effect is clarified.
Shop the CLX THERABAND Resistance Bands:
This summary was prepared by Dr. Juan Colado, one of the clinicians who completed the research study. His summary was supplemented by Performance Health employee, Michelle Kok, for publication on this blog.
Medical Disclaimer: The information provided on this site, including text, graphics, images, and other material are for informational purposes only and are not intended to substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other healthcare professional with any questions or concerns you may have regarding your condition.








 France
France Australia
Australia