Key Takeaways
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation devices send electrical pulses to stimulate muscles and relieve pain
- A variety of conditions, like perioperative pain and acute pain, can benefit from TENS therapy
- TENS is safe for most users, but you should consult a medical professional before using a TENS device
Top Products in This Article
Looking for pain relief? TENS might be the solution.
This alternative to medication has existed in its conceptual form since 60 A.D. when physicians used electrical fish from the ocean for pain relief. Nowadays TENS has evolved into a much safer, more effective form of treatment. Modern TENS units and functionality are credited to American neurosurgeon, Dr. C. Norman Shealy thanks to his research on transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation.
If you’re introducing a patient to TENS treatments in your clinic or recommending at-home TENS pain relief, share this guide to answer your patient’s commonly asked questions!
Patient's Guide of TENS Unit Muscle Stimulation
Frequently Asked Questions
What conditions can TENS therapy be used for?
What does the research say about TENS therapy for pain relief?
Is TENS painful? What does using a TENS machine feel like?
What are my options for TENS units?
Where should I place TENS electrodes?
When should I purchase replacement TENS electrodes?
Is TENS therapy pain relief effective for everyone?
What does TENS stand for?
TENS stands for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation.
What is TENS?
A TENS device consists of a main unit that controls the electrical pulses and electrodes which are placed on the user’s skin. It’s a type of therapy used for pain relief.
How do TENS units work?
A TENS battery-powered device delivers alternating current via electrodes that are placed on the skin around the painful area. Most devices allow you to set the pulse frequency and intensity. The stimulation activates a complex neural network in your body, providing an analgesic (pain relieving) effect and relieving your pain.
If you want to get really scientific, TENS analgesia is maintained through the periaqueductal gray (PAG), rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM), and spinal cord, as well as central mechanisms. High-frequency TENS produces analgesia by activating mechanisms in the central nervous system involving opioid GABA and muscarinic receptors. While low frequency TENS uses pathways that activate the opioid, GABA, serotonin, and muscarinic receptors.
What conditions can TENS therapy be used for?
TENS machines can benefit a variety of conditions for effective pain relief. In some cases, it can be a helpful alternative to more invasive forms of treatment like surgery. It also offers an alternative to medications and opioids. Talk to a medical professional before using a TENS unit.
Research has shown that TENS is effective at relieving pain from:
- Perioperative pain (pain before, during, or after surgery)
- Osteoarthritis
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Some forms of acute pain
Evidence also suggests it may help relieve pain from:
- Fibromyalgia
- Spinal cord injury
As research continues, it may find further evidence for using TENS to relieve other types of pain.
The Cleveland Clinic and the University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics state that TENS is also commonly used to treat:
|
|
TENS should not be used if you have:
- A cardiac pacemaker or defibrillator
- In-dwelling pumps or monitors
- Spinal cord stimulator
- Any implanted metallic or electronic device
- Talk to your doctor if you have cancer, epilepsy, diabetes, cognitive impairment, or are pregnant. Also talk to your doctor if you are allergic to certain metals, to ensure you are using the proper electrodes
- Read the TENS unit user manual for other precautions and contraindications
What does the research say about TENS therapy for pain relief?
In addition to what conditions TENS may be useful for, studies have also looked at the best practices for effective pain relief.
Key takeaways include:
- Both high and low frequency TENS have been shown to produce pain relief when used at a strong intensity. However, because they activate different opioid receptors, high frequency TENS may be more effective for people taking opioids.
- Effective pain relief for chronic conditions may be limited if you use the same frequency and intensity daily because the repeated application can create a tolerance. To avoid this and prolong the pain relief, varying TENS parameters may help (whether you use the high or low frequency TENS).
- Applying TENS electrodes at acupoints may increase the analgesic effect
- Using TENS during movement/activity may be the most beneficial for pain relief
Is TENS painful? What does using a TENS machine feel like?
TENS should not feel painful. You should set the intensity at a level that is strong, but tolerable. It may feel like a tingling, buzzing, or muscle twitching sensation. As you grow accustomed to the feeling, you may be able to increase the intensity.
Is TENS safe?
TENS is safe for most users, but you should consult a medical professional before using a TENS device. One possible negative side effect is skin irritation from the patches.
While you can’t get shocked by turning the device as high as it will go, you may feel discomfort at the highest levels. Because it is an electrical device, you can get shocked if the unit gets wet, if you touch bare wires, or if you reposition/remove the patches before during the device off.
Clinicians and patients can learn more about precautions and contraindications in this summary document or by reading the full study.
What are my options for TENS units?
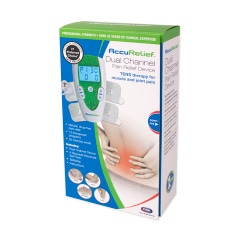
Home TENS Unit: Dual Channel TENS
The Dual Channel TENS unit allows you to use two or four electrode pads at a time. Use four electrodes at once to surround a larger treatment area. With pre-set programs and 25 levels of adjustable intensity, this unit is a highly versatile option for pain relief.
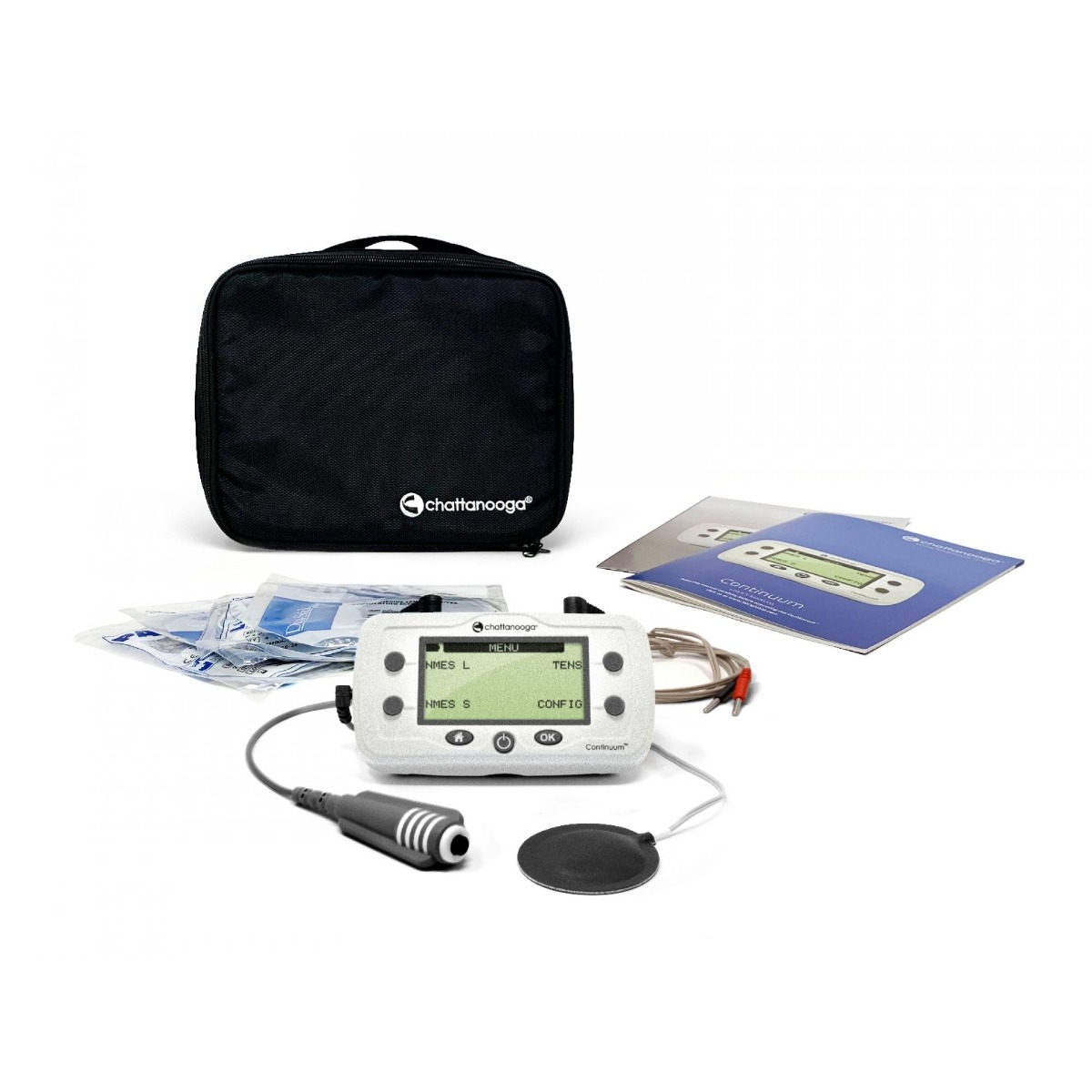
NMES + TENS for Clinicians: Chattanooga Continuum
Designed for clinicians, the Chattanooga Continuum can be used for both NMES (neuromuscular electrical stimulation) and TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation). It includes pre-programmed options and custom options including treatment time, waveform type (symmetrical or asymmetrical), pulse rates & durations, cycling type, and more.
How do I use a TENS unit?
This is a general overview on using a TENS unit. Consult your device’s manual for specific use instructions.
- Make sure the TENS unit is off, then insert the batteries/charge the unit
- Remove the electrode patches from the bag
- Push the lead wires all of the way into the connectors on the patches (no bare metal should be exposed)
- Insert the lead wire plugs into the TENS unit sockets
- Take the patches off of the plastic backing (saving it for future use)
- Place the patches on clean, dry skin
- Place the patches so they surround the painful area
- Make sure the patches are at least one inch apart
- Make sure the patches don’t touch each other or any metal objects (such as jewelry or belt buckles)
- Turn the TENS unit on
- Follow the treatment plan your doctor has given you
- Set the intensity so it is strong, but comfortable. If the sensation lessens as time goes on, your body may be getting used to it - increase the intensity until it is once again strong, but comfortable
- Turn the unit off, remove the lead wires from the electrode patches, remove the electrodes from your skin and replace them on the plastic backing before placing them in the plastic bag to save for future use
Do not use the patches:
- On any part of your face, head, or neck
- On both sides of the chest/trunk at the same time
- Internally
- Over broken skin wounds or lesions or rashes
- Over or near tumors or cancerous lesions
- Directly over the spine/backbone
- On skin that does not have normal sensation/feeling
Consult your user manual for further instructions and contraindications.
Where should I place TENS electrodes?
Talk to your doctor about the most effective electrode placement when using a TENS unit and follow their recommendation. Most TENS units also include a placement guide that can aid you in proper electrode placement.
10 Tips for TENS Pad Placement
- Electrode for TENS units should be placed on the fleshy area of your body, not the boney area
- Always use two pads (single channel) or four pads (dual channel), one pad will not be effective
- Changing the distance between the pads or the direction of the pads can change the electrical sensation
- Pads can be placed vertically, horizontally, or angulated
- TENS electrodes should not touch and should be placed at least one inch apart (as the distance between them increases, the effectiveness decreases)
- Avoid placement over the knee or other joints as it can negatively impact the pad’s adherence
- When pain extends a greater distance across the body (like sciatica pain), place one pad vertically at the top of the pain and another pad vertically at the bottom of the pain
- When pain is focused in a smaller area (like calf pain), place the pads parallel on each side of the pain
- When the pain overlaps a joint (like the elbow), place the pads on the muscle tissue just above and just below the joint in a horizontal and parallel direction
- When the pain is wide (like between your shoulders), place the pads vertically to the right and left of the spine. If it extends further above/below the shoulder area, angulate the pads
Be sure to follow your doctor’s recommendations regarding proper electrode placement.
When should I purchase replacement TENS electrodes?

Most TENS electrodes are designed for single-patient use. You shouldn’t share your electrodes with other family members or friends. Many electrodes can be used up to ten times. Check the user manual to see the recommended replacement electrodes for your unit.
Is TENS therapy pain relief effective for everyone?
A TENS massage may not be an effective form of pain relief for all conditions. These pain relief alternatives can be used in addition to or instead of TENS.
Stopain provides relief for muscle aches and pain, bruises, arthritis, and more. The topical analgesic is available in gel, spray, and roll-on forms.
Cold therapy can help relieve pain from recent injuries, while heat therapy is best for more chronic conditions. Try both by using a SISSEL Hot-Cold Pack, which can be frozen or microwaved for soothing pain relief.
Bon Vital Complete Massage Creme
Massage is another option for pain relief. You or your partner can use this massage creme to enhance your massage by increasing the glide and hydrating your skin.
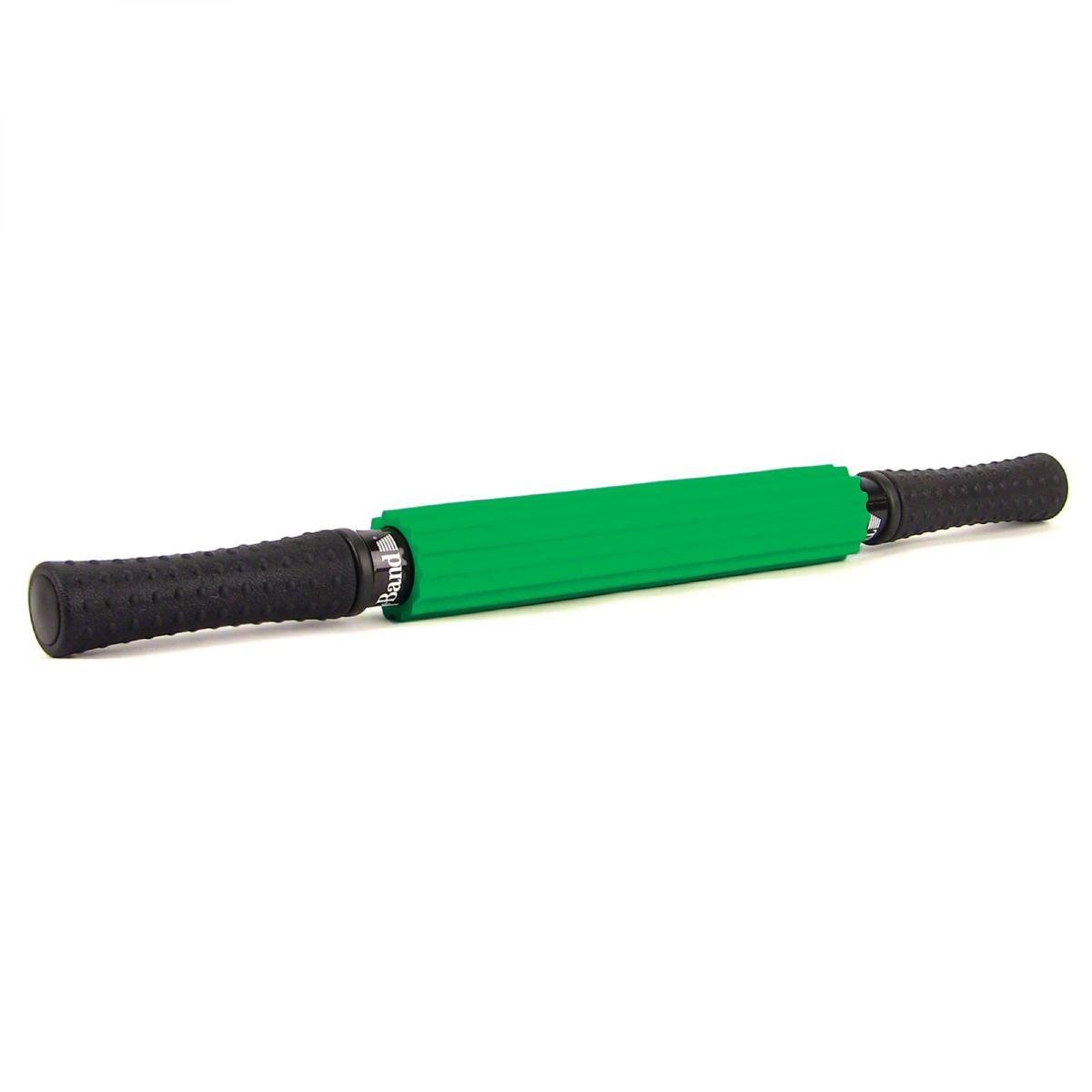
This tool is excellent for self-massage. The roller can be used for targeted myofascial release of trigger point pain or for a more general all-over massage.
Foam rolling allows you to apply a deep tissue massage to release muscle knots and relieve inflammation.
Medical Professionals

Talk to your doctor about seeing other medical professionals that can help. Physical therapists, chiropractors, athletic trainers, and other medical professionals may also offer treatments that can help reduce or eliminate your pain.
References
- Vance, C. G., Dailey, D. L., Rakel, B. A., & Sluka, K. A. (2014). Using TENS for pain control: the state of the evidence. Retrieved from https://bit.ly/31MCb4r
- University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics. (2019). Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulator (TENS). Retrieved from https://bit.ly/2HhI5kl
- Teoli, D. & An, J. (2019). Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS). Retrieved from https://bit.ly/2ULHC1U
- Cleveland Clinic. (2020). Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS). Retrieved from https://cle.clinic/2OM7reC
- Wheeler, T. (2019). Can TENS Help Your Pain? WebMD. Retrieved from https://wb.md/2SjLvtq
- Mannheimer, J.S. (2014). TENS Unit Pad Placement: 10 Tips for Effective Use. Retrieved from https://bit.ly/2SkJUmQ
Medical Disclaimer: The information provided on this site, including text, graphics, images and other material, are for informational purposes only and are not intended to substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other healthcare professional with any questions or concerns you may have regarding your condition.








 France
France Australia
Australia